Categories
Values
Ensure Security and Business Continuity
Reduce Costs
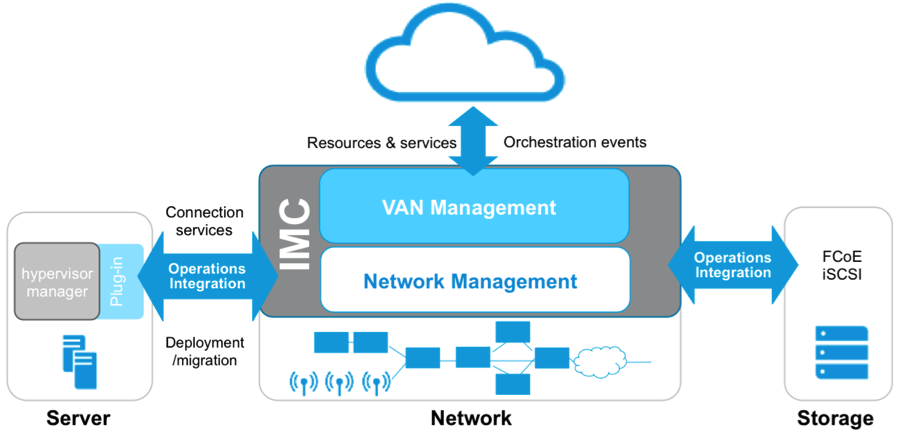
HPE Intelligent Management Center (IMC)
HPE Intelligent Management Center (IMC) delivers integrated management of the central devices of campus networks and data center networks.
About Product
Description
Network managers, engineers, and operators face complex challenges in their mission to deliver a reliable
and available network infrastructure. IMC is a comprehensive management platform that simplifies how IT
staff can successfully meet these challenges.
IMC was built from the ground up to support the FCAPS model for comprehensive management of the
network infrastructure. In addition, IMC was designed to support the ITIL operational center of excellence IT
practices model. IMC’s single–pane management paradigm enables end-to-end business management of IT
services to address the stringent demands of today’s mission-critical enterprise IT operations.
IMC provides scalability by supporting distributed and hierarchical system architectures, through additional
operating system and database support to meet the requirements of complex networks. IMC uses a SOA
model to provide full resource, service, and user management. Its modular design enables the integration of
traditionally separate management tools. IMC enables enterprises to expand their infrastructure
management in scale and to seamlessly accommodate new technologies at the same time.
IMC base platform features
IMC consists of a base platform and service components that offer additional functionalities. The base
platform provides administrators and operators with the basic and advanced functionality needed to
manage IMC and the devices managed by IMC.
The IMC base platform provides the following functions:
• Administrative controls for managing IMC and access to it. This includes granting or restricting
operator access to IMC features through operator and operator group management.
The base platform also includes features for the system-wide management of device data collection
and information shared by all IMC modules. Features include:
The creation and maintenance of device, user, and service groups
Device vendor, series, and device model information.
SNMP MIB management and other system-wide settings and functions. See "Role based
administrative controls."
• A broad feature set for network device management, from the ability to manage SNMP, Telnet, and
SSH configurations on a device to configuring Spanning Tree and PoE energy management for
managed switches and much more. See "Resource management."
• Management of the configuration and system software files on devices managed by IMC. This includes
storing, backing up, base-lining, comparing, and deploying configuration and software files. See
"Configuration and change management."
• Real time management of events and the translation of events into faults and alarms in IMC. This
includes creating, managing, and maintaining alarm lists, trap and Syslog filters and definitions, and
configurations for notifications of alarms. See "Real time fault management."
• Monitoring, reporting, and alarming on the performance of the network and the devices that comprise
it. This includes managing global and device specific monitors and thresholds as well as creating views
and reports for displaying performance information. See "Performance monitoring and management."
• Access control list (ACL) management. This includes creating and maintaining ACL templates,
resources, and rule sets and deploying ACL rule sets to devices managed by IMC. It also includes
monitoring and leveraging ACLs that exist on devices for deployment to other network devices. See
"Global ACL management."
• Monitoring and managing security attacks and the alarms they generate. See "Security monitoring."
• Global management of VLANs on all devices that support VLANs, managed by IMC. See "Global
VLAN management."
These are the functional areas of IMC’s base platform. In addition, the IMC framework and suite of services
also includes service components for extending the scope and reach of IMC’s ability to manage the network
infrastructure.
Scheme of work